C-Section
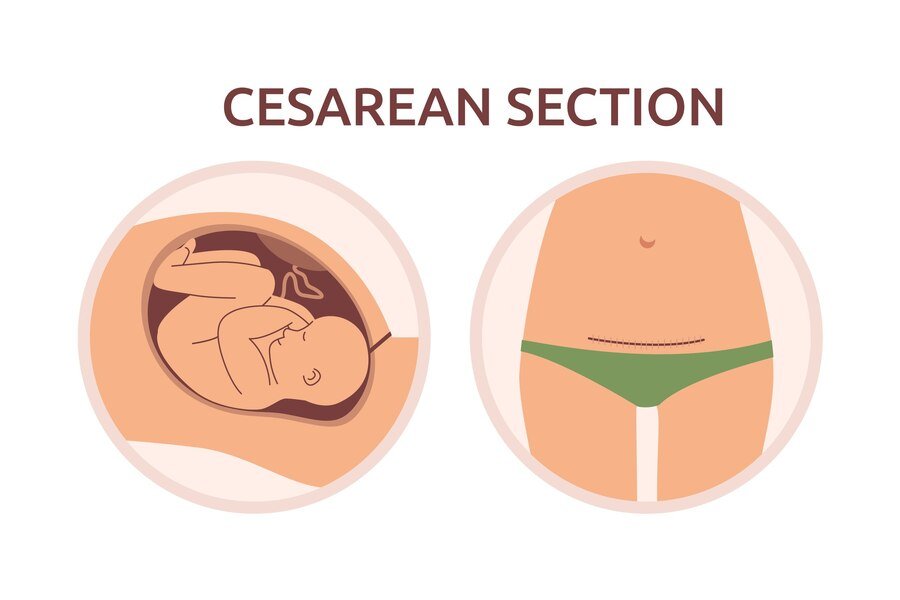
A Cesarean section, commonly referred to as a C-section, is a surgical procedure used to deliver a baby when vaginal delivery is not possible or safe for the mother or baby. This may occur due to various factors such as fetal distress, breech presentation, multiple births, placenta previa, or maternal health conditions like high blood pressure or certain infections. During a C-section, an incision is made in the mother's abdomen and uterus, allowing the baby to be safely delivered. The procedure is typically performed under regional anesthesia, such as an epidural or spinal block, to numb the lower half of the body while the mother remains awake.
While C-sections are generally considered safe and can be life-saving in certain situations, they do carry risks like any surgical procedure. These risks include infection, bleeding, blood clots, injury to surrounding organs, and complications with anesthesia. Additionally, C-sections may have implications for future pregnancies, such as an increased risk of uterine rupture or placenta previa in subsequent pregnancies. Despite these risks, C-sections are sometimes necessary to ensure the health and safety of both the mother and baby. It's important for expectant mothers to discuss their birth preferences and any concerns with their healthcare provider to make informed decisions about their delivery options.
Services features
- Safe Delivery Environment
- Emergency Response
- Anesthesia Options
- Surgical Expertise
- Mother-Baby Bonding Support
- Postoperative Care
.jpeg)



